How do solar panels turn sunshine into electricity?

How do solar panels turn sunshine into electricity?
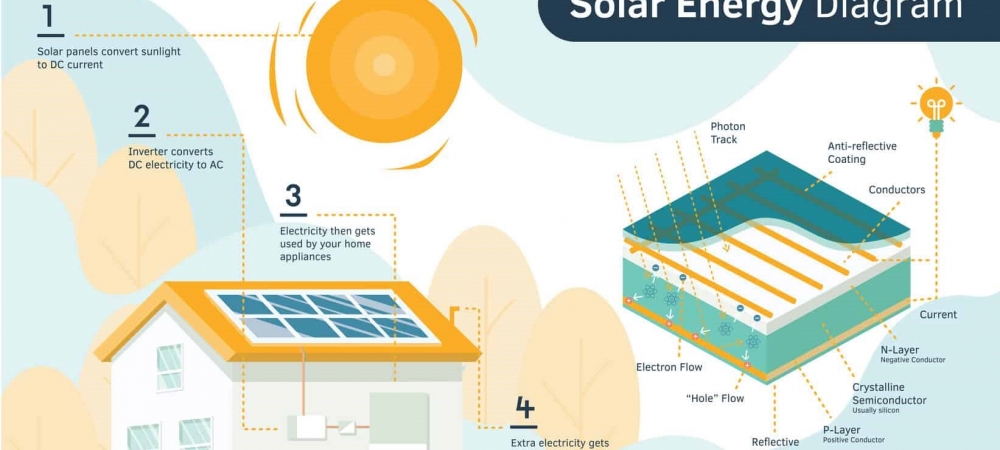
Solar (or photovoltaic) cells convert the sun’s energy into electricity. Whether they’re powering your calculator or appliances, they rely on the photoelectric effect: the ability of matter to emit electrons when a light hits it.
PV cells are made from silicon. Silicon is a semi-conductor, meaning that it has some of the properties of metals and some of those of an electrical insulator, making it a key ingredient in solar cells.
Sunlight is composed of miniscule particles called photons, which radiate from the sun. As these hit the silicon atoms of the solar cell, they transfer their energy to loose electrons, knocking them off the atoms, and creating an electrical current.
Watch video here: link
SUN FOR FREE © 2025, All rights reserved - Site by: MIP
Scroll to Top